- Products
-
Identity and access management
-
Unified service management
-
Unified endpoint management and security
-
IT operations management and observability
-
Security information and event management
-
Advanced IT analytics
-
Low-code app development
-
Cloud solutions for enterprise IT
-
IT management for MSPs
Active Directory
management Manage, track, and secure Active DirectoryIdentity governance
and administrationOrchestrate user identity management and access controls for Zero TrustPrivileged access
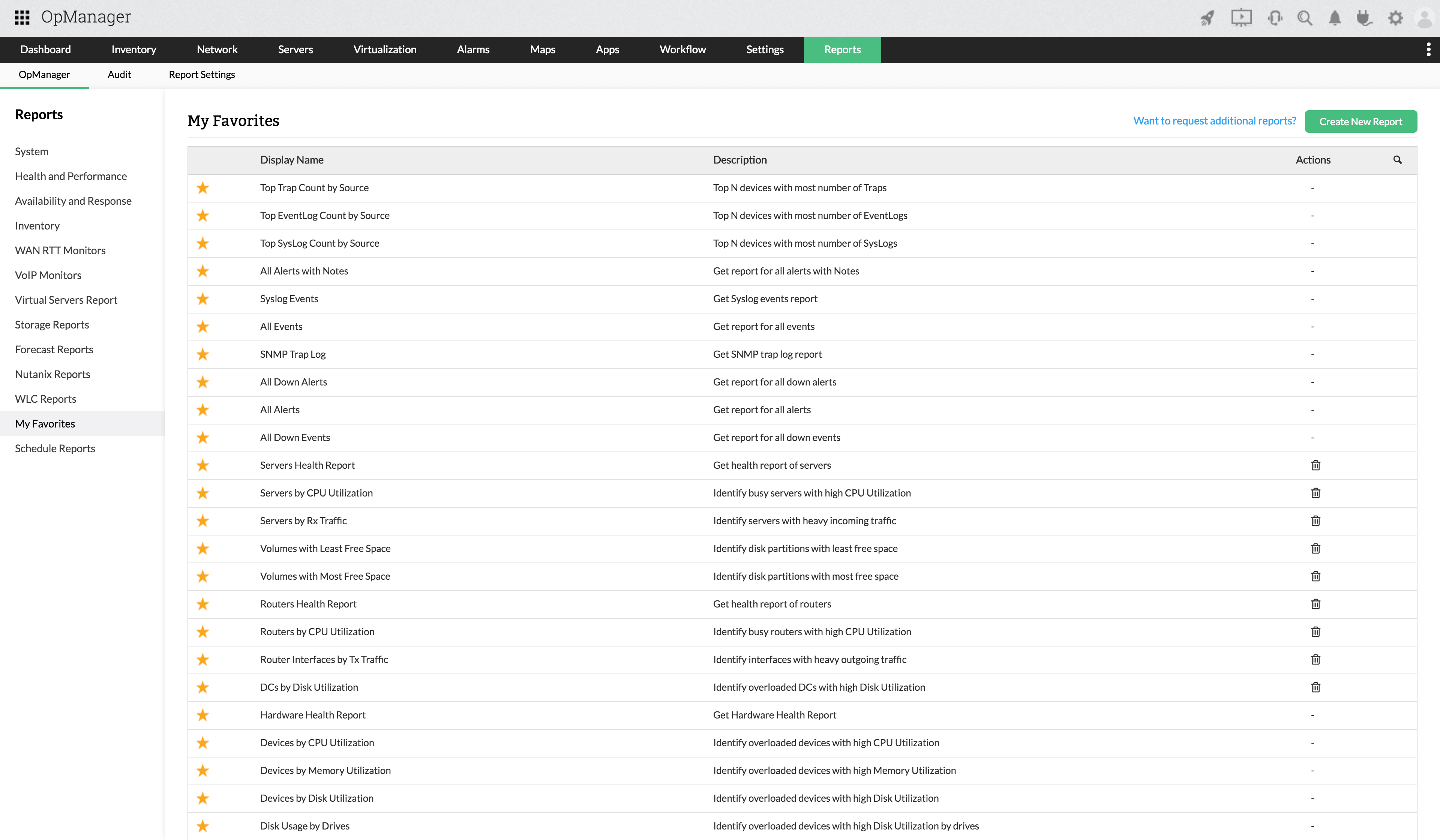
managementControl and secure privileged access to critical enterprise systemsRelated free tools Hybrid AD management toolsActive Directory Academy- ADManager Plus
Active Directory, Microsoft 365, and Exchange management and reporting
- ADAudit Plus
Hybrid AD, cloud, and file auditing; security; and compliance
- ADSelfService Plus
Identity security with adaptive MFA, SSPR, and SSO
- Exchange Reporter Plus
Reporting, auditing, and monitoring for hybrid Exchange and Skype
- RecoveryManager Plus
Active Directory, Microsoft 365, and Exchange backup and recovery
Enterprise and IT service
managementDeliver a consistent employee experience across business functionsCustomer service
managementBuild a one-stop portal for customers with efficient account managementIT asset
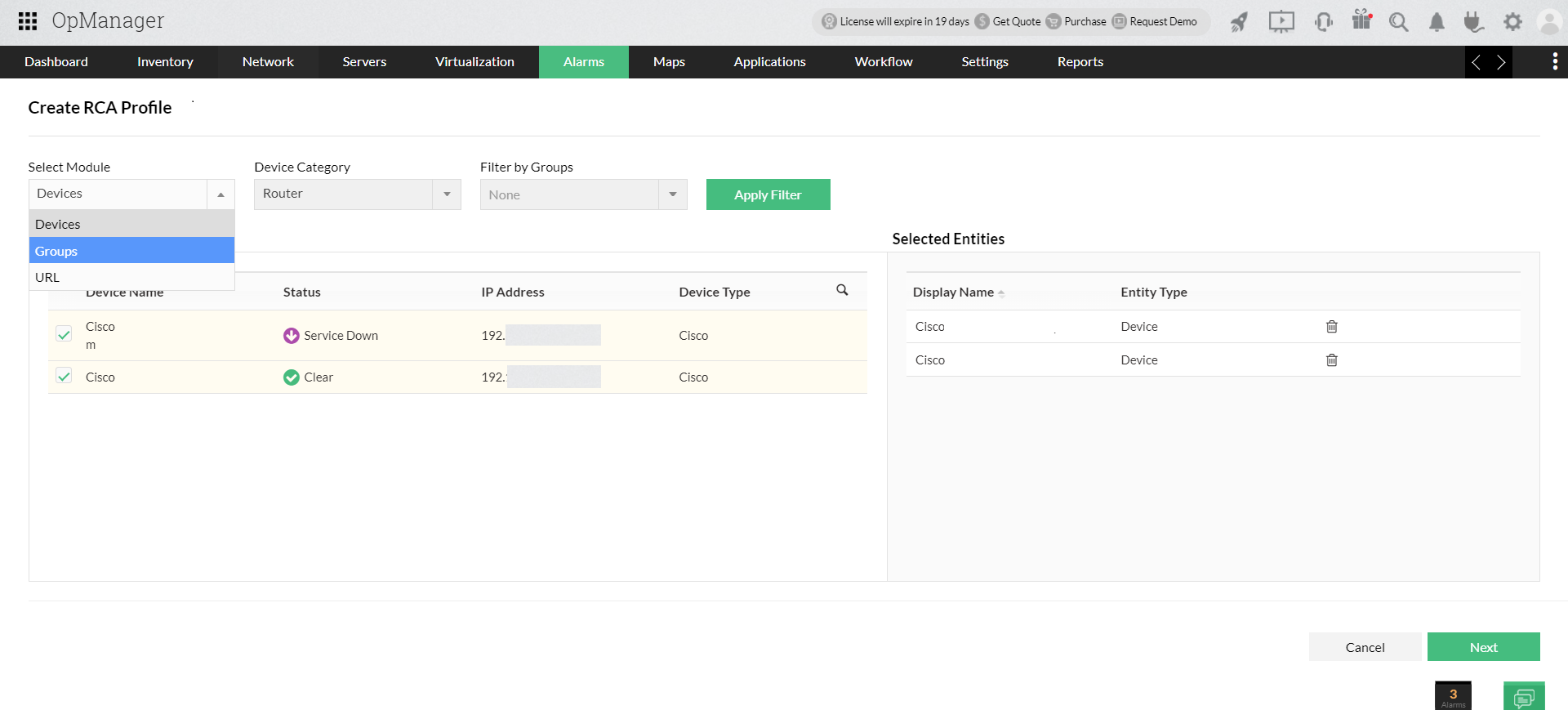
managementCentralize and automate the complete IT asset life cycleSIEM Spot, investigate, and neutralize security threats
Log and compliance managementGain deeper visibility into security events and ensure compliance
Security auditingAudit Active Directory, cloud platforms and files to enhance your security posture
SIEM Hubspot- ADAudit Plus
Hybrid AD, cloud, and file auditing; security; and compliance
- SharePoint Manager Plus
SharePoint reporting and auditing
- M365 Security Plus
Microsoft 365 security
- Cloud Security Plus
Cloud security monitoring and analytics
- DataSecurity Plus
File auditing, data leak prevention, and data risk assessment
- FileAnalysis
File security and storage analysis
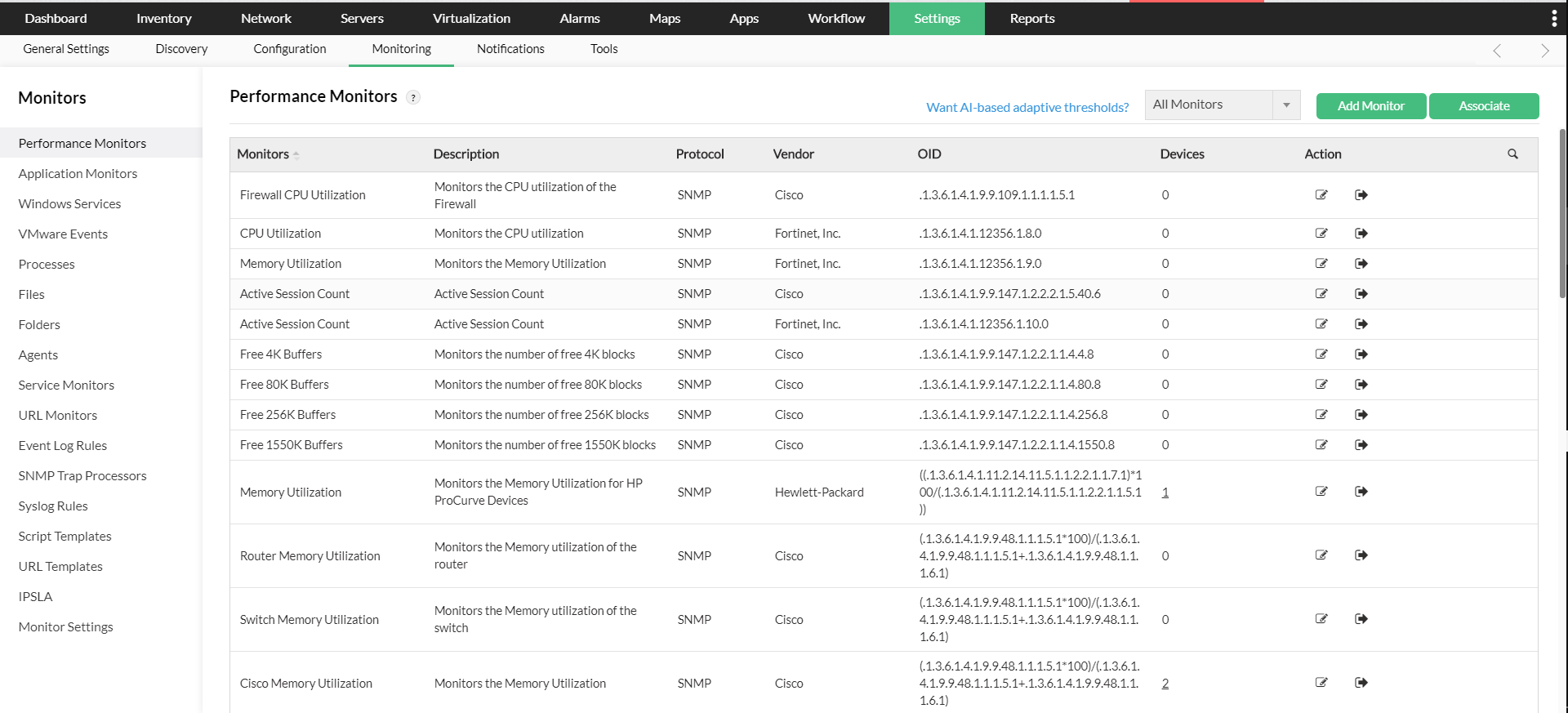
Endpoint management and protection platform (UEM and EPP)Secure and manage endpoints to protect your IT assets effectively
Endpoint managementAchieve intelligent IT device management with zero user intervention
Endpoint securityDefend against threat actors with proactive and reactive measures
Free Windows admin tools Free system tools- Patch Manager Plus
Automated patching across multiple OSs and over 850+ third-party apps
- Patch Connect Plus
Simplified third-party patch deployment via ConfigMgr and Intune
- Mobile Device Manager Plus
Seamless mobile device management from onboarding to retirement
- Remote Access Plus
Remote troubleshooting with integrated chat, voice, and video
- OS Deployer
Automated OS image creation and seamless role-based deployment
- Vulnerability Manager Plus
Prioritization-focused enterprise vulnerability management
- Application Control Plus
App control and endpoint privilege management software
- Device Control Plus
Data theft prevention with strict peripheral device control
- Browser Security Plus
Browser security with isolation, lockdown, and activity tracking
- Endpoint DLP Plus
Sensitive data protection and compliance for endpoint devices
- Ransomware Protection Plus New
Real-time ransomware mitigation and file recovery for business continuity
- Malware Protection Plus New
Next-gen antivirus software for threat detection and breach prevention
Full-stack observability and digital experience monitoringAchieve end-to-end visibility, proactive issue resolution, and enhanced security
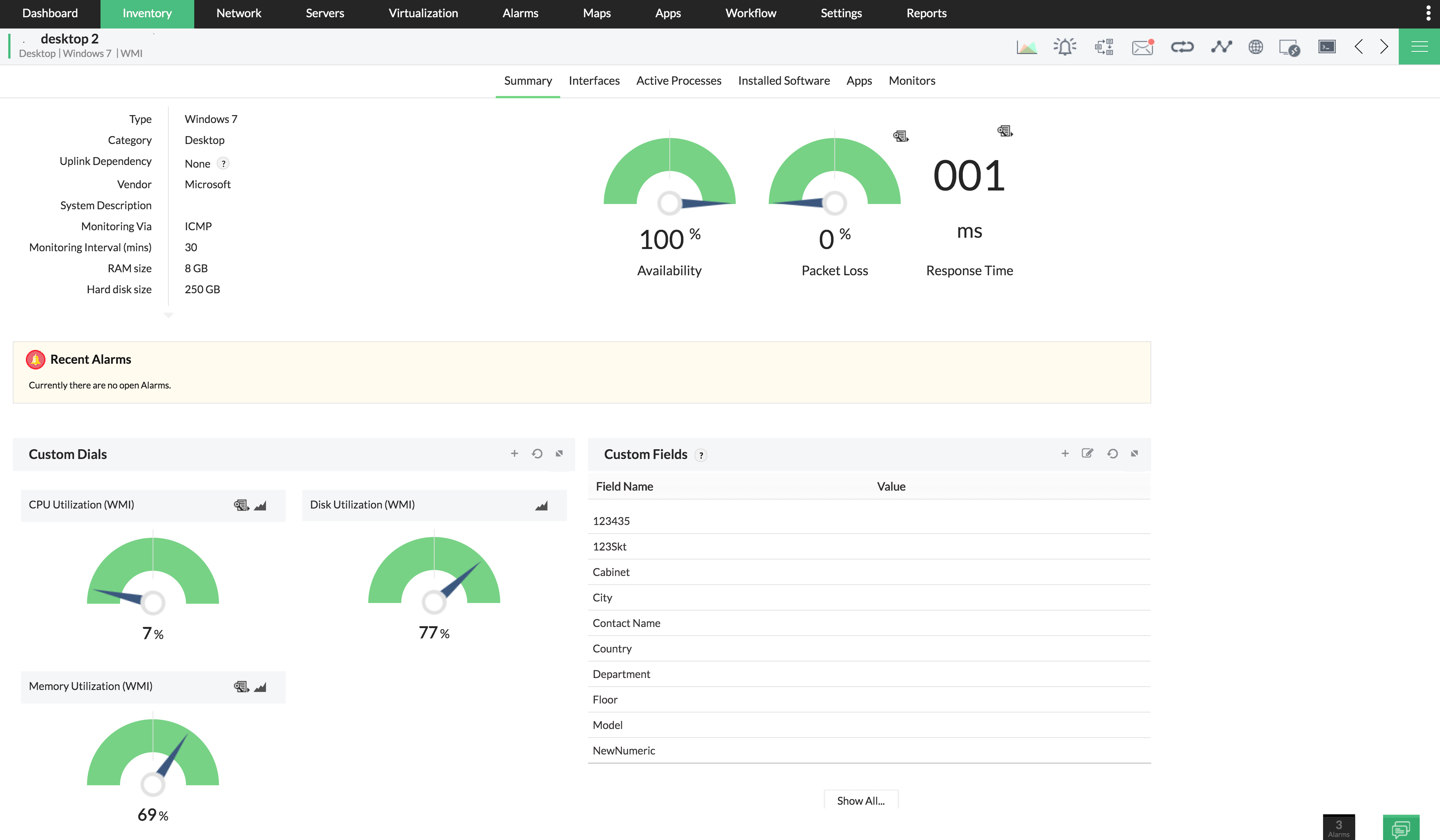
Network and server
performance monitoringEnsure network, server, and storage reliability with AI-powered insightsIT incident
managementEfficiently manage and resolve IT incidents while ensuring transparencyRelated free tools- OpManager Plus
Full-stack observability with AIOps and digital experience monitoring
- Site24x7
AI-powered, all-in-one SaaS platform for observability and digital experience monitoring
- Applications Manager
Digital experience, application performance, and infrastructure monitoring
- Digital Risk Analyzer
All-in-one vendor risk assessment tool to ensure domain security
- OpManager
Network, server, and storage performance monitoring
- NetFlow Analyzer
Bandwidth monitoring and traffic analysis
- Network Configuration Manager
Network change and configuration management
- Firewall Analyzer
Firewall rule, configuration, and log management
- OpUtils
IP address and switch port management
- AlarmsOne
Centralized IT alert management
- Site24x7 StatusIQ
Status pages for real-time status and incident communication
DNS and DHCP managementOptimize IP address and domain management
Cloud cost managementRight-size and take control of your cloud costs
IT analyticsConnect to your IT applications and visualize all facets of your IT
Cloud-native solutions for IT managementMonitor, manage, audit, and secure your multi-cloud
and hybrid infrastructureBusiness applications for ITBoost productivity and improve team collaboration
Our DatacentersAWS marketplace Azure marketplace- Identity360
A cloud-native identity platform for workforce IAM
- ServiceDesk Plus
Full-stack service management for enterprises
- AssetExplorer
IT asset management with an integrated CMDB
- Endpoint Central
Unified endpoint management and security
- Mobile Device Manager Plus
Comprehensive mobile device management
- Remote Access Plus
Enterprise remote access
- Patch Manager Plus
Automated multi-OS patch management
- Site24x7
Full-stack monitoring for IT admins, DevOps, and SREs
- Site24x7 StatusIQ
Status pages for real-time status and incident communication
- CloudSpend
Cloud cost management for modern software teams
- SaaS Manager Plus
SaaS management platform to maximize ROI
- AlarmsOne
Centralized IT alert management
- Log360 Cloud
Secure your IT infrastructure and prove compliance from the cloud
- Analytics Plus
AI-powered unified analytics platform to correlate all IT data
- CloudDNS
An all-in-one DNS management service to keep your business online
- Zoho Creator
Low-code application development platform
- Zoho Assist
Remote support software
- Zoho Projects
Collaborative project management
- Zoho Sprints
Agile project management
- Zoho Workplace
All-in-one collaboration tool for unified communication
- Zoho Mail
Secure email hosting solution for businesses
- Zoho Meeting
All-in-one video conferencing solution for remote business meetings
- Zoho Lens
All-in-one AR remote assistance software solution for remote collaboration.
Custom solution builderBuild tailor-made apps to automate operations at your organization
Solutions for MSPsGrow your MSP business with scalable and secure IT management solutions
- RMM Central
Unified network monitoring and endpoint management for MSPs
- ADManager Plus MSP
Unified Active Directory management and reporting solution for MSPs
- Log360 MSSP
Unified SIEM solution for MSSPs
- EventLog Analyzer MSSP
Log management and advanced threat intelligence for MSSPs
- PAM360
Complete privileged access security for enterprises
- Password Manager Pro
Privileged password management
- ServiceDesk Plus MSP
Full-stack service management for MSPs
-
- Store
- Partners
- Affiliate
- Support
-
- Desktop Management | On-premises | Active Directory Management and Reporting | Remote Access Software | Asset Management | Customer Support Software | Help Desk Software | Remote Support Software | OS Deployment | Active Directory Auditing | Identity Password Management & IT Self-Service | Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting | Active Directory Backup & Recovery Tool | SharePoint Reporting & Auditing | File server auditing & data discovery | Active Directory Identity Management (AD360) | Application Performance Monitoring (APM) | Website Monitoring & Server Monitoring (Cloud) | Network Monitoring Software | Bandwidth Monitoring & Traffic Analysis | Microsoft 365 Management and Reporting| Mobile device management | Browser security & management | Privileged Access Management | Log Management & IT Compliance Tool | Unified SIEM Tool & SOAR solution