How is an IT help desk different from an
IT service desk?
April 04 | 12 mins read

The terms help desk and service desk are used across various industries and within multiple departments like HR, facilities, and payroll. However, it's in the realm of IT support that these two terms are used the most frequently and sometimes interchangeably.
While there are some similarities between the help desk and the service desk, there are also a plethora of differences in terms of their capabilities and functions. If you are just starting out in IT support and looking to refresh your knowledge of ITSM concepts, this article will help you accurately distinguish between a help desk and a service desk.
What is a help desk?
The help desk is the first point of contact for users (customers or employees) who are experiencing technical difficulties. It provides reactive, break/fix solutions and troubleshoots individual user issues, such as a slow workstation, faulty printer, or network issue. Help desks primarily focus on a single ITIL® practice: incident management. Their main objective is therefore limited to resolving IT issues quickly.
In contrast, service desks take on a broader role, overseeing various ITSM practices such as incident, service request, problem, change, and release management.
What are the benefits of a help desk?
- A single point of contact: A help desk provides a single, easily accessible point of contact for all IT-related issues. This simplifies the support process for users and ensures consistent service.
- Quick resolutions and user satisfaction: For organizations with simple IT needs, a help desk can provide quick resolutions, improving user satisfaction.
- A cost-effective entry point: If you're in a smaller organization or working with a tight budget, a help desk is a practical, affordable way to handle your IT support requirements.
Help desk metrics
Help desk performance can be evaluated using the following essential metrics:
- First contact resolution: The percentage of issues resolved upon first contact with the end user
- The ticket volume: The total amount of support tickets received during a specific timeframe; tracking this helps with resource planning
- End-user satisfaction: End users' satisfaction with help desk services as measured via surveys
- The mean time to resolve: The average duration from first contact to the final resolution of an issue
What is a service desk?
According to ITIL, a service desk is "the single point of contact between the service provider and the users. A typical service desk manages incidents and service requests and also handles communication with the users."
While this definition may sound a bit simple, a typical service desk goes beyond simply resolving IT issues. It adopts a proactive approach to managing IT services, focusing on aligning IT with overall business goals. This is achieved by implementing changes to the IT infrastructure, identifying the root causes of repetitive incidents, and building seamless service request fulfillment processes. It's not just about fixing incidents; it's about designing, managing, and delivering IT services. This service-centricity distinguishes a service desk from a help desk, which is more issue-centric.
What are the essential ITSM and ITIL practices managed by
a service desk?
Here are some of the key ITSM practices that are a part of a service desk's responsibilities:
Incident management
Service request management
Problem management
Change enablement
Release management
Service-level management
Knowledge management
Self-service and automation
Reporting and analytics
Continual service improvement
Integrating other ITIL practices
Security and compliance
What are the benefits of a service desk?
The service desk is a crucial component of ITSM that provides a single point of contact for users to report issues and request services while enabling IT teams to implement changes to their IT infrastructure and fix the root causes of incidents. It offers numerous benefits, such as improved end-user satisfaction, streamlined communication, and efficient problem resolution. Here are some other key benefits of a service desk in an organization:
- Proactive problem prevention: A service desk actively identifies and addresses the root causes of recurring issues. This reduces downtime and improves overall service stability.
- Enhanced employee experiences: A service desk helps meet employee experience demands through the timely fulfillment of service requests. It also improves the uptime of applications and services by fixing the root causes of repetitive incidents.
- Improved alignment between IT and business goals: With a focus on core ITSM practices like problem management, change enablement, and knowledge management, the service desk reduces incidents, builds new IT services, and improves existing ones.
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Through standardized processes, automation, and knowledge management, a service desk streamlines IT operations and improves efficiency. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Service desk metrics
When it comes to measuring and optimizing service desk operations, there are metrics that can help your team identify inefficiencies. These include the ticket volume, the agent utilization rate, service-level agreement (SLA) compliance, and the cost per ticket. For a detailed breakdown, we recommend you browse our guide on service desk metrics.
Understanding the key differences: Help desks vs. service desks
Although the help desk and service desk both aim to resolve user issues, they differ significantly in their scope, focus, and long-term goals. If your organization is considering which option to choose, it is important to understand these distinctions. Here are the key differences between the two:
| Parameter | Help desk | Service desk |
| Focus | Incident management (limited to handling break/fix operations) | ITSM (provides end-to-end service delivery)—other departments' service desks may also implement ITSM best practices, ultimately leading to enterprise service management (ESM). |
| Scope | Reactive (focused on immediate issue resolution) | Proactive (focused on preventing problems and improving services) |
| Goal | Restore service quickly | Meet employee needs and expectations and improve business outcomes through IT |
| SLAs | May have informal service targets | Has formal SLAs with defined metrics and responsibilities |
| Services offered | Troubleshooting and basic technical assistance | A wide range of operations, including incident, service request, change, problem, and knowledge management |
| ITIL alignment | Incident management | A comprehensive ITIL framework covering incident management, request fulfillment, problem management, change enablement, release management, and more |
| Level of complexity | Handles simple, common issues | Handles both simple and complex issues, changes, service requests, problems, and more |
| Technology used | Ticketing software with basic automation capabilities | Advanced ITSM software with workflow automation, AI, and self-service capabilities |
How does a typical help desk workflow differ from that of a service desk?
While both a help desk and service desk aim to provide technical support, their workflows and responsibilities vary significantly. In this section, we will showcase the differences between typical help desk and service desk workflows.
Help desk workflows
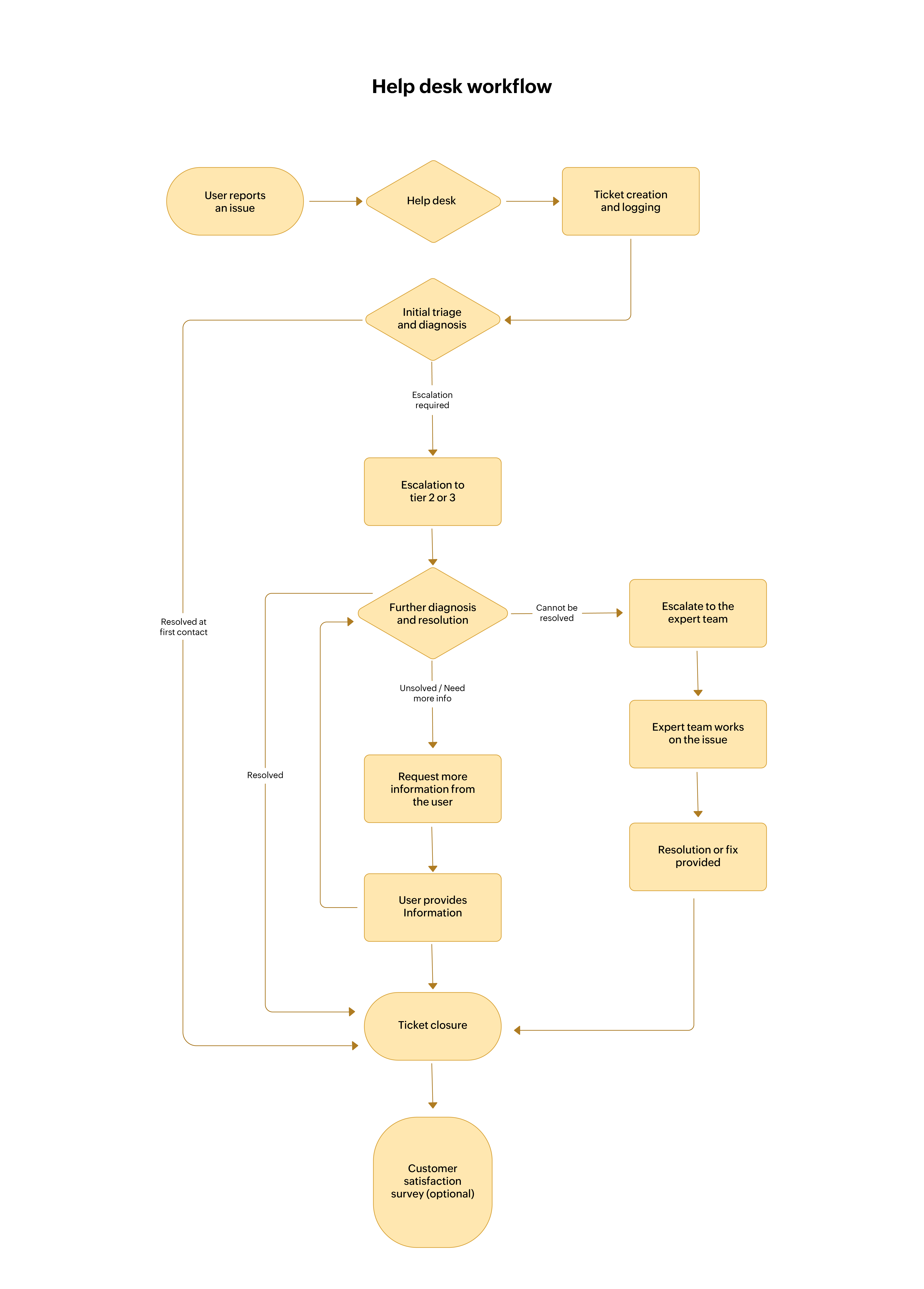
A help desk workflow starts with an end user reporting an issue, extends into troubleshooting, and ends with a fix for that specific issue. Typically, a help desk follows the workflow demonstrated below:
Service desk workflows
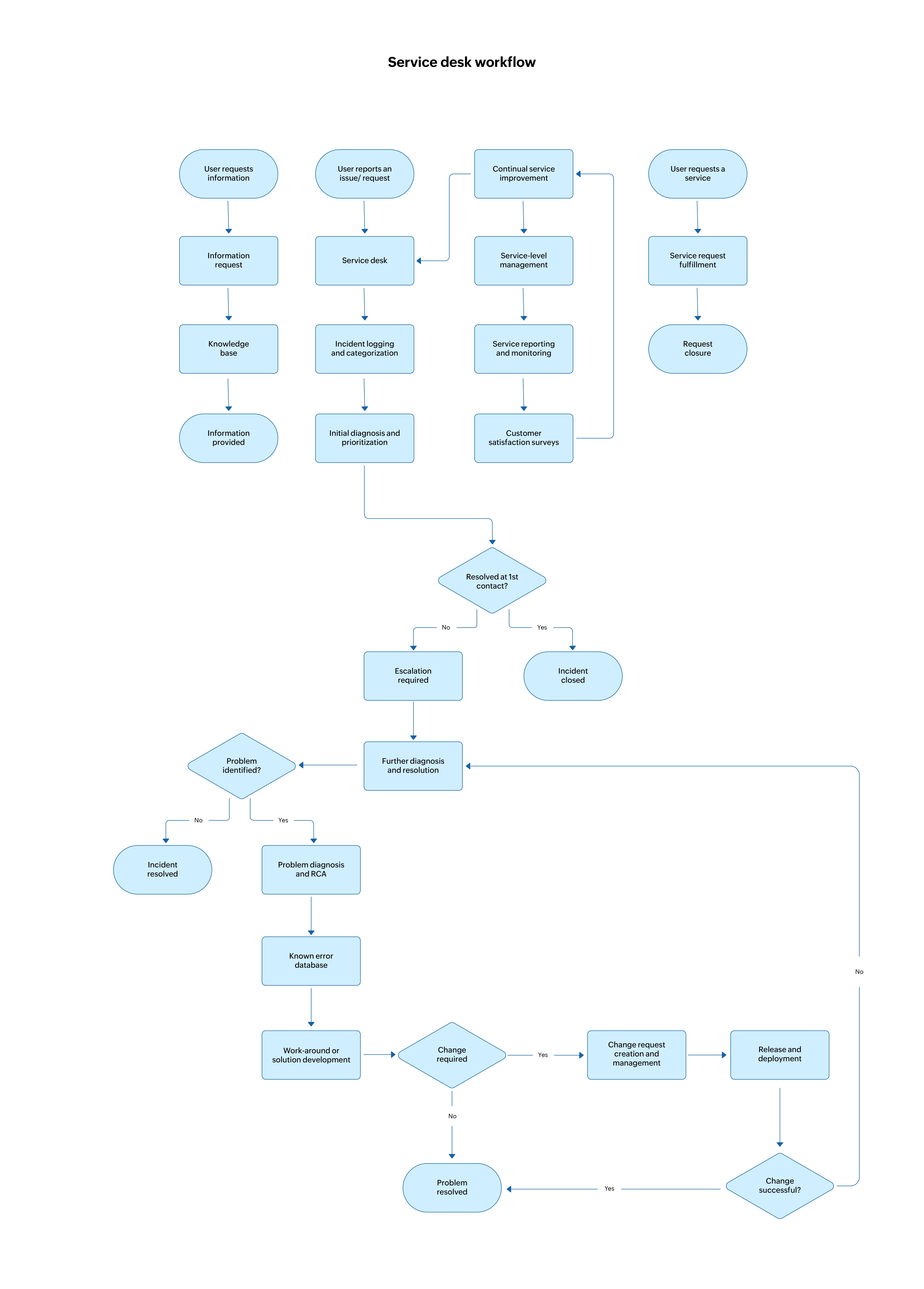
A typical service desk's workflow is an amalgamation of multiple ITSM practices, like incident, problem, and change management. Here's how a typical service desk operates:
What are some of the use cases solved by help desks
and service desks?
In the first table, we examined the differences between help desks and service desks based on various criteria. To gain a better understanding of how these differences manifest in practical situations, take a look at the following use cases that illustrate the approaches of help desks and service desks:
Help desk use cases
- Password resets: A user calls, unable to log in. The help desk verifies the user's identity and performs a password reset, granting them immediate access. The incident is closed after the successful reset.
- Low internet speeds: A user complains about a slow internet speed. The help desk agent walks the user through basic troubleshooting steps, like restarting the modem and checking the Wi-Fi signal. If the problem persists, the ticket is escalated to a higher-tier support agent.
Service desk use cases
- Multiple networking incidents: Multiple users experience network outages. The service desk initiates problem management, performing RCA to identify the underlying issue. The team then implements a permanent fix, preventing future occurrences.
- Employee onboarding: A new employee is hired. The service desk coordinates onboarding tasks across HR, IT, and facilities departments using automated workflows. The service desk ensures all the necessary systems and resources are provisioned before the employee's start date.
Which approach is right for you?
Choosing between a help desk and a service desk depends on several key factors. There's no one-size-fits-all answer, so careful consideration of your organization's specific needs is crucial.
Factors to consider
- The size of your organization: Smaller organizations with limited IT and a small userbase may opt for a help desk, while larger ones with complex IT and numerous employees need a service desk.
- Your IT maturity level: Organizations with a basic IT setup and a focus on keeping systems running may find a help desk adequate. As IT becomes more critical to business operations, and the need for strategic alignment grows, a service desk becomes essential. A service desk's focus on proactive problem management and service improvement becomes crucial at higher maturity levels.
- Your business needs and goals: If your primary goal is to simply fix problems as they arise, a help desk might suffice. However, if your business relies heavily on IT, and you need to ensure high availability, high end-user satisfaction, and continuous service improvement, a service desk is the better choice. Consider if you need IT to be a strategic driver of your business; if so, a service desk is the clear winner.
- Your budget: Help desks typically require a smaller investment in terms of software, training, and staffing. Service desks, with their advanced ITSM tools and broader scope, usually involve a larger financial commitment. However, the long-term return on investment from a service desk, through increased efficiency and reduced downtime, can be substantial.
What are the capabilities to look for in help desk and
service desk solutions?
When choosing a help desk or service desk solution, it's important to think about what features will best meet your organization’s needs. From efficient ticket management to robust reporting features, the right solution can truly boost your IT support and service management efforts. In this section, we’ll explore some key features to look for when checking out different help desk or service desk options.
| Feature | Help desk solution | Service desk solution |
| Incident management |
|
|
| Service request management | N/A |
|
| Problem management | N/A |
|
| Change management | N/A |
|
| Knowledge management |
|
|
| Asset management | N/A |
|
| Automation and integrations |
|
|
| Automation and integrations |
|
|
| AI and ML |
|
|
| Reporting and analytics |
|
|
Special considerations for AI capabilities in help desk and service desk solutions
AI capabilities are no longer a luxury but a necessity for both help desk and service desk solutions. Having AI's predictive analytics in your help desk or service desk can help you identify and resolve issues proactively before they impact users, and AI chatbots can help you provide instant conversational support 24/7. Furthermore, agentic AI promises to revolutionize IT support by autonomously making decisions, carrying out complex tasks without any human intervention, and enabling more personalized user experiences.
Why is ServiceDesk Plus the ideal help desk or service desk solution for your specific needs?
Now that you understand the differences between the two, it's imperative to assess your organization's IT maturity and opt for help desk software or service desk software accordingly. It is also essential to select a solution that is future-ready, aligns with your current needs, and is capable of supporting your future business growth.
ServiceDesk Plus is one such platform; powered by AI, it combines ITSM, IT asset management, and a CMDB with ESM. It also comes with enterprise-grade AI capabilities, including predictive, conversational, and generative capabilities that foster high performance in help desks and service desks.
For organizations seeking to establish a strong foundation with basic help desk capabilities, the Standard edition of ServiceDesk Plus is an excellent starting point. It provides all the necessary tools for incident management and reporting. When your needs evolve, and you're ready to embrace a more mature service desk approach, ServiceDesk Plus will seamlessly scale with you. Upgrading to higher editions unlocks advanced ITIL features, like problem management, change management, knowledge management, and robust reporting, empowering you to deliver exceptional IT services and drive business success.
Explore ServiceDesk Plus today and discover how it can transform your IT support!




